Study Material
1. Resources and Development
1. Multiple choice questions.
i) Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
A) Intensive cultivation B) Deforestation ( )
C) Over irrigation D) Overgrazing
A. (C) Over irrigation.
ii) In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practised? ( )
A) Punjab B) Plains of Uttar Pradesh
C) Haryana D) Uttarakhand
A. (D) Uttarakhand.
iii) In which of the following states black soil is predominantly found? ( )
A) Uttar Pradesh B) Maharashtra
C) Rajasthan D) Jharkhand
A. (B) Maharashtra.
2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
i) Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
A. a) Black Cotton Soil cover the plateaus of Maharashtra, Saurashtra, Malwa, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
b) Black soil is ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil.
ii) What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
A. Alluvial soil is found in the eastern coastal plains particularly in the deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri rivers.
Features of this soil :
1) Alluvial soils as a whole are very fertile.
2) Mostly these soils contain adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime.
3) These are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereal and pulse crops.
iii) What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
A. 1) Contour Ploughing along the contour lines can decelerate the flow of water down the slopes.
2) Terrace cultivation restricts erosion.
3) Strips of grass are left to grow between the crops. This breaks up the force of the wind. This method is known as strip cropping.
3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
i) Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
A. 1) Land resources in India are divided into agricultural land, forest land, land meant for pasture and grazing, and waste land.
2) Waste land includes rocky, arid and desert areas, and land used for other non-agricultural purposes such as housing, roads and industry.
3) About 54% of the total land area is cultivable or fallow, 22.5% is covered by forests, and 3.45% is used for grazing.
4) The rest is waste land, with traces of miscellaneous cultivation.
5) The land under forest has not increased since 1960-61.
The reasons are -
a) Demand for more land to expand agriculture, mainly after Green Revolution, developmental works and infrastructural facilities, led to clearance of forest areas.
b) Industrialisation and urbanisation also decreased the forest area.
c) Thus, land under forest has increased by only about 4% since 1960-61.
ii) How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
A. 1) Technical and economical development led to more consumption of resources which increased production.
2) Production increased the employment opportunities and increased living standard of people. It led to Urbanization.
3) Employment opportunities increased the purchasing capacity of the people.
4) The purchasing capacity of the people created and recognized new needs of the people.
5) The development of transportation technologies has enabled people and goods to move across greater distances at faster speeds.
6) This has increased the demand for fuels such as oil and gas, as well as the materials required to build and maintain these vehicles.
7) Technical and economic development has led to the growth of modern agriculture, which requires large amounts of water, fertilizers, pesticides, and energy to produce crops.
8) The increased demand for food has also led to deforestation and the conversion of natural ecosystems into agricultural land.
9) Economic development has led to increased construction which require large amounts of materials such as cement, steel, and glass.
10) The production of these materials can have significant environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions, water and air pollution, and habitat destruction.
11) Thus technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources.
project/activity
1 . Make a project showing consumption and conservation of resources in your locality.
A. Resources : Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, is called a resource. It should be technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable. Only then, it can be termed as a 'Resource'. Most of the resources are God's gift., that is nature' gift.
Oil, coal, natural gas, metals, stone and sand are natural resources. Other natural resources are air, sunlight, soil and water. Animals, birds, fish and plants are natural resources as well.
Kinds of Resources : Resources are characterized as renewable or non-renewable; a renewable resource can replenish itself at the rate it is used, while a non-renewable resource has a limited supply. Renewable resources include timber, wind, and solar while non-renewable resources include coal and natural gas.
Consumption of Resources : Natural resources like water, soil, clean air and mineral deposits provide the basis for our quality of life. Studies show that these resources are vastly overused today. This pressure on natural resources could further intensify in future as the size of the economy and global population will continue to increase.
Overuse of Natural Resources : The overuse of natural resources not only has negative consequences for the environment, for example, through soil sealing or the pollution of water bodies, but also for the economy, which relies on a secure supply of raw materials. Because the predicted population and economic growth will further intensify this effect, a significant increase in the efficient use of existing resources is essential.
Resource consumption : Resource consumption is about the consumption of non-renewable, or less often, renewable resources. Specifically, it may refer to: water consumption, energy consumption, electric energy consumption.
In our area the resources are very limited. We are using them in a proper way. Non-renewable resources can be conserved but not possible to reproduce.
Ways to conserve natural resources :
1) It is important to conserve such resources.
2) Water is conserved by minimal use of it.
3) The electricity use should be checked to prevent its waste.
4) Recycling renewable materials is a good way to conserve them.
5) Producing fewer new materials reduces waste.
6) It aids in the reduction of groundwater and air pollution.
7) Composting is an excellent method for converting food scraps into useful materials for the garden.
8) Composting reduces soil erosion and enriches the soil while reducing the need for watering.
2. Have a discussion in the class - how to conserve various resources used in your school.
A. A discussion is conducted between two groups in the classroom. Their decisions are mentioned hereunder-
R. Devyansh group :
1) Switch off the lights and fans when they are not in use.
2) Turn off the taps properly.
3) Don't pluck grass from the school ground.
S. Amirah group :
1) Use steel or copper water bottles instead of plastic bottles.
2) Use paper covers or cotton bags.
3) Don't waste paper. Use magic slates.
3. Imagine if oil supplies get exhausted, how will this affect our life-style?
A. 1) If oil supplies get exhausted, this will affect our life-style significantly.
2) People would not be able to go from one place to another.
3) Many of the activities of people depend on petroleum products like petrol, diesel, LPG, CNG etc.
4) Most of the world transport is dependent on fossil fuel. It would also be crippled.
5) There would be conflicts between countries and communities for control of alternative sources of energy.
6) World trade and economy would be negatively affected as supply of goods will break down causing scarcity.
4. Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
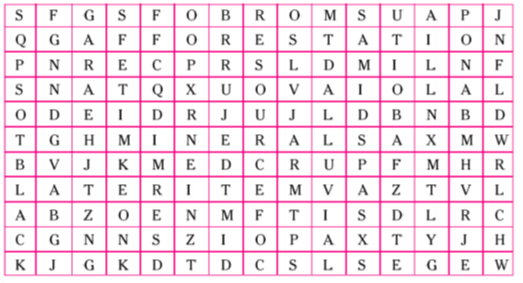
i) Natural endowments in the form of land, water, vegetation and minerals.
ii) A type of non-renewable resource.
iii) Soil with high water retaining capacity.
iv) Intensively leached soils of the monsoon climate.
v) Plantation of trees on a large scale to check soil erosion.
vi) The Great Plains of India are made up of these soils.
A. i) Resource ii) Minerals
iii) Black iv) Laterite
v) Afforestation vi) Alluvial
Questions given in the Lesson
1. Can you identify and name the various items used in making life comfortable in our villages and towns. List the items and name the material used in their making.
A. Villages :
Clothes to wear : Cotton, synthetic fibers, wool, silk, etc.
Furniture : Wood, steel, rubber, etc.
Houses : Bricks, cement, wood, glass, other building materials.
Bicycles and motorcycle : Steel, rubber, etc.
Kerosene stove : Steel, brass, etc.
Bulbs and tubelights : Copper, tungsten, glass, etc.
Towns :
Clothes to wear : Cotton, synthetic fibers wool, silk, etc.
Furniture : Wood, steel, rubber, etc.
Houses : Bricks, cement, wood, glass, other building materials.
Cooking gas stove and cylinder : Steel, brass, rubber, etc.
Cars and motorcycles : Steel, plastics, brass, etc.
Fans, room coolers and air conditioners : Steel, copper, plastics, etc.
Consumer durables like refrigerators and TV sets : Steel, copper, plastics, glass, etc.
Find out
2. What resources are being developed in your surroundings by the community/village panchayats/ward level communities with the help of community participation?
A. Biogas plants, biofertilisers plant, usage of solar power panels, rain water harvesting are developed in our Ithavaram village, Nandigam mandal in NTR district.
3. Can you name some resource rich but economically backward regions and some resource poor but economically developed regions? Give reasons for such a situation.
A. 1) Jharkhand state is rich in mineral resources. However, it is economically backward. The reasons are -
a) It was originally mostly populated by tribals who were uneducated.
b) Due to the rocky terrain, there is very little agricultural land.
c) Lack of industrial development in earlier times compared with the rest of India.
2) The Mumbai region of Maharashtra state is poor in natural resources, but is highly economically developed due to the following reasons :
a) It is the commercial hub of India with the maximum amount of local, national and international trade transactions .
b) It has a large number of industries established from a number of years.
c) It has a very efficient transportation system for people and materials.
d) The people living and working there are well-educated and earning the maximum compared to any other area in India.
4. Find out reasons for the low proportion of net sown area in these states.
A. 1) Net sown area in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, and Manipur is low mainly due to the hilly and rocky terrain.
2) They are also largely covered by dense forests, which will need to be cut to develop agriculture and that leads to deforestation.
3) Andaman and Nicobar Islands are covered by dense tropical forests and so the net sown area is low.
